Computer Accessories
Computer Accessories
Exam Focus: This unit extensively covers input and output devices, their types, and ergonomic considerations. Expect questions requiring you to differentiate between devices, explain their functions, and discuss ergonomic design principles.
4.1 The Input Accessories
Input accessories are peripheral devices that allow users to feed data and instructions into a computer system. They convert human-readable input into a machine-understandable binary format.
Keyboard Devices
The most common text-entry device, allowing users to input characters, numbers, and symbols, and to control computer functions. Keyboards are peripheral input devices modeled after the typewriter keyboard, using an arrangement of buttons or keys to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. They convert human-readable input into machine-understandable binary format.
Keyboards come in various types, each designed for specific needs, ergonomics, and environments. The standard layout is QWERTY, named after the first six letters on the top row of keys.
- QWERTY (Standard): The most common keyboard layout, originating from typewriters. It arranges keys to prevent jamming by placing commonly used letters apart. Used for general typing, text editing, and command input. Available in full-size (104-105 keys), laptop-size (reduced travel and keys), and compact forms.
- Ergonomic Keyboards: Designed to minimize muscle strain, fatigue, and injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome. Features include split designs (separated into left and right halves), negative tilt (angled downwards), tenting, and integrated wrist rests. They promote a more natural hand and wrist position, reducing ulnar deviation and shoulder elevation.
- Mechanical Keyboards: Use individual mechanical switches under each key, providing tactile feedback and audible clicks. Switches vary (e.g., Cherry MX: linear, tactile, clicky). Popular for gaming and typing due to durability (up to 50 million keystrokes), customization, and responsiveness. More expensive but preferred by enthusiasts.
- Virtual Keyboards: On-screen keyboards displayed on touchscreens or monitors, controlled by mouse, stylus, or touch. Used on smartphones, tablets, and for accessibility. Software like Windows On-Screen Keyboard or mobile virtual keyboards. Useful in sterile environments or for users with mobility impairments.
- Other Types: Flexible (silicone, water/dust-proof), handheld (ergonomic, held like game controllers), thumb-sized (for PDAs), multifunctional (with LCD displays, biometric readers), projection (laser-projected keys), optical (LED/photo sensors).
Keyboards connect via USB, PS/2, Bluetooth, or wireless (RF/IR). They include alphanumeric keys, modifiers (Shift, Ctrl, Alt), function keys, navigation keys, and multimedia controls. Illumination (backlit) aids low-light use, especially in gaming.
- Application: Text editing, command input, gaming, programming, accessibility.
Point and Draw Devices
Pointing devices allow users to control the position of a pointer (cursor) on the screen for selection, navigation, drawing, and interaction with graphical user interfaces. They translate physical movements into digital signals, enabling precise control. Classified as direct (e.g., touch) or indirect (e.g., mouse), absolute or relative, isotonic, isometric, or elastic.
- Mouse: A hand-held pointing device that detects two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. It translates movement into cursor motion on screen. Types include mechanical (roller-ball), optical (LED/infrared), laser, wireless (Bluetooth/RF), ergonomic (vertical, contoured), gaming (high DPI, programmable buttons). Features buttons (left/right/middle), scroll wheel, and gestures. Essential for desktop computing, gaming, and CAD.

- Trackball: A stationary pointing device with an exposed ball that users rotate with fingers, thumb, or palm. The ball's rotation moves the cursor. Often used in CAD workstations, laptops, or for one-handed operation. Advantages: no desk space needed, precise control, ergonomic for certain users. Can be wireless and include buttons.

- Touchpad/Trackpad: A flat, touch-sensitive surface on laptops detecting finger contact via capacitive sensors. Supports multi-touch gestures (scroll, zoom, swipe). Relative positioning, with buttons or tap-to-click. Integrated into most laptops; some external versions exist. Pressure sensitivity and palm rejection enhance usability.

- Stylus/Light Pen: A pen-shaped device for precise input on touchscreens or graphics tablets. Provides absolute positioning, pressure sensitivity, and tilt detection for drawing. Used in digital art, note-taking (e.g., tablets like Wacom), and signatures. Light pens detect screen phosphors; modern styluses use capacitive or active digitizer technology.
These devices follow Fitts' Law: selection time depends on target size and distance. Ergonomic designs reduce strain; wireless options offer flexibility.
Yoke

A yoke is a specialized input device resembling an aircraft control column or steering wheel, used primarily for flight simulation and driving games. It provides realistic control over pitch (up/down) and roll (left/right) in flight simulators, or steering in racing games. Often includes throttle levers, rudder pedals, and buttons for additional controls. Connected via USB, it offers force feedback for immersion. Essential for aviation training software and gaming.
Data Scanning Devices
Exam Question Alert: Be ready to explain different types of data scanning devices and their applications.
Data scanning devices are input peripherals designed to read text, images, or codes directly from a source document or object and convert them into digital data that a computer can process. These devices automate data entry, reduce human error, and speed up various processes, making them indispensable in many industries.
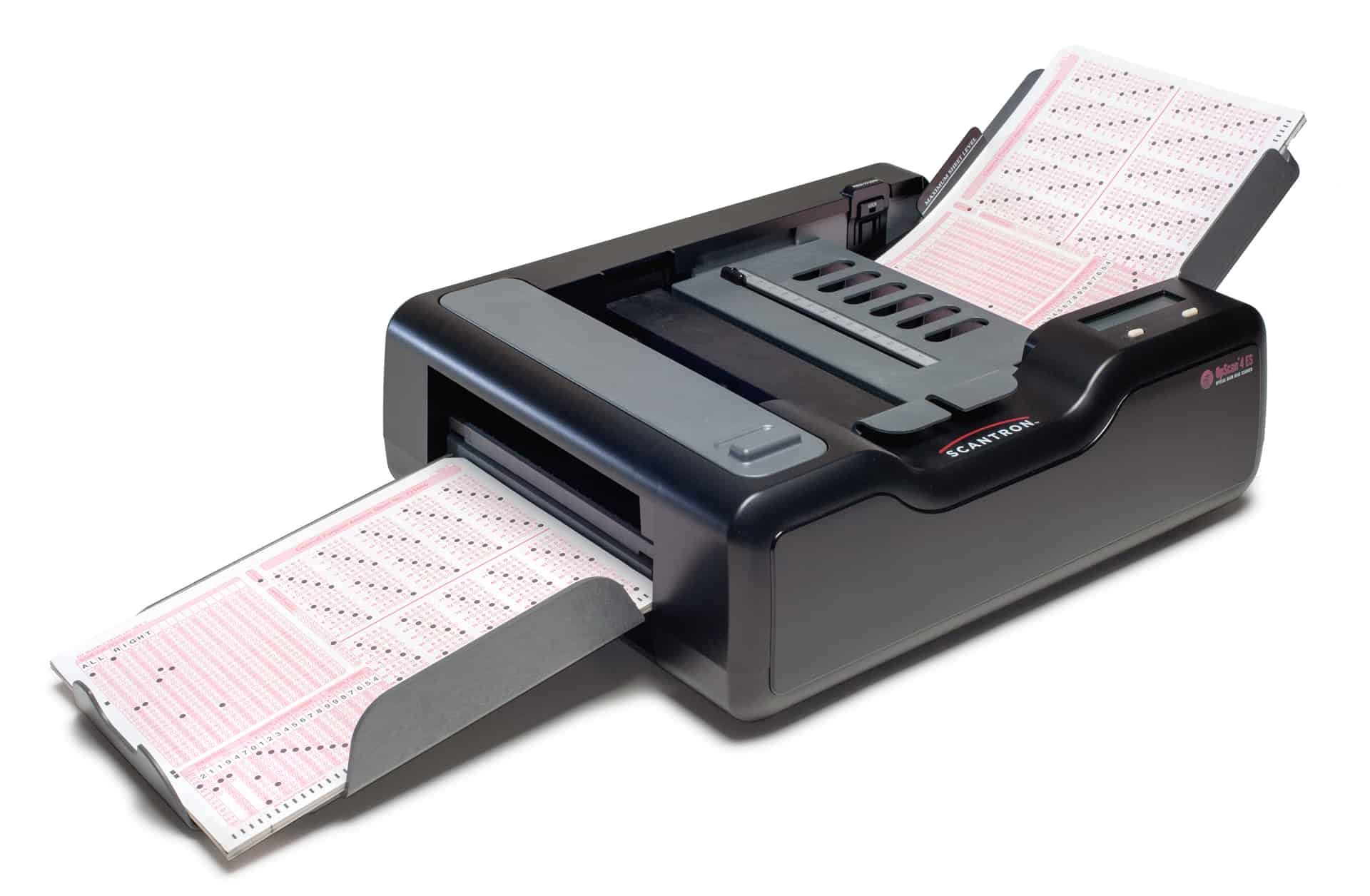
- Optical Mark Reader (OMR): OMR devices detect the presence or absence of a mark in a predefined position on a form. They are commonly used for reading multiple-choice test sheets, surveys, and other forms where responses are indicated by filling in bubbles or boxes. OMR is highly efficient for processing large volumes of standardized forms quickly.

- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): OCR technology scans images of typed, handwritten, or printed text and converts them into machine-encoded text. This allows for the digital editing, searching, and storage of documents that were originally in physical format. Applications include digitizing books, processing invoices, and converting scanned documents into editable text files.

- Bar Code Reader: Barcode readers (or scanners) are electronic devices that can read and decode barcodes, which are optical machine-readable representations of data. They are widely used in retail for point-of-sale systems, inventory management, and tracking items. Different types exist, including pen-type readers, laser scanners, and CCD readers.

- Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR): MICR is a technology used primarily by the banking industry to facilitate the processing of cheques and other documents. It reads special characters printed with magnetic ink, typically found at the bottom of cheques, which include bank codes, account numbers, and cheque numbers. This technology helps in fast and accurate processing of financial transactions.
- Image Scanner: A general-purpose scanner that converts physical documents, photographs, or other images into digital files. These digital images can then be stored, edited, or shared electronically. Flatbed scanners and handheld scanners are common types.
Digitizer (Graphics Tablet)

A graphics tablet, or digitizer, is an input device consisting of a flat surface (pad) and a stylus (pen) for drawing or writing. It digitizes hand-drawn images and sends them to the computer as digital data. Provides absolute positioning, pressure sensitivity, tilt detection, and programmable buttons. Types include resistive, capacitive, electromagnetic (e.g., Wacom Intuos). Larger tablets offer more workspace; wireless options available. Cursor (puck) for precise tracing in CAD.
- Application: Graphic design, digital art, architectural drawings, photo editing, animation, CAD/CAM.
Microphone
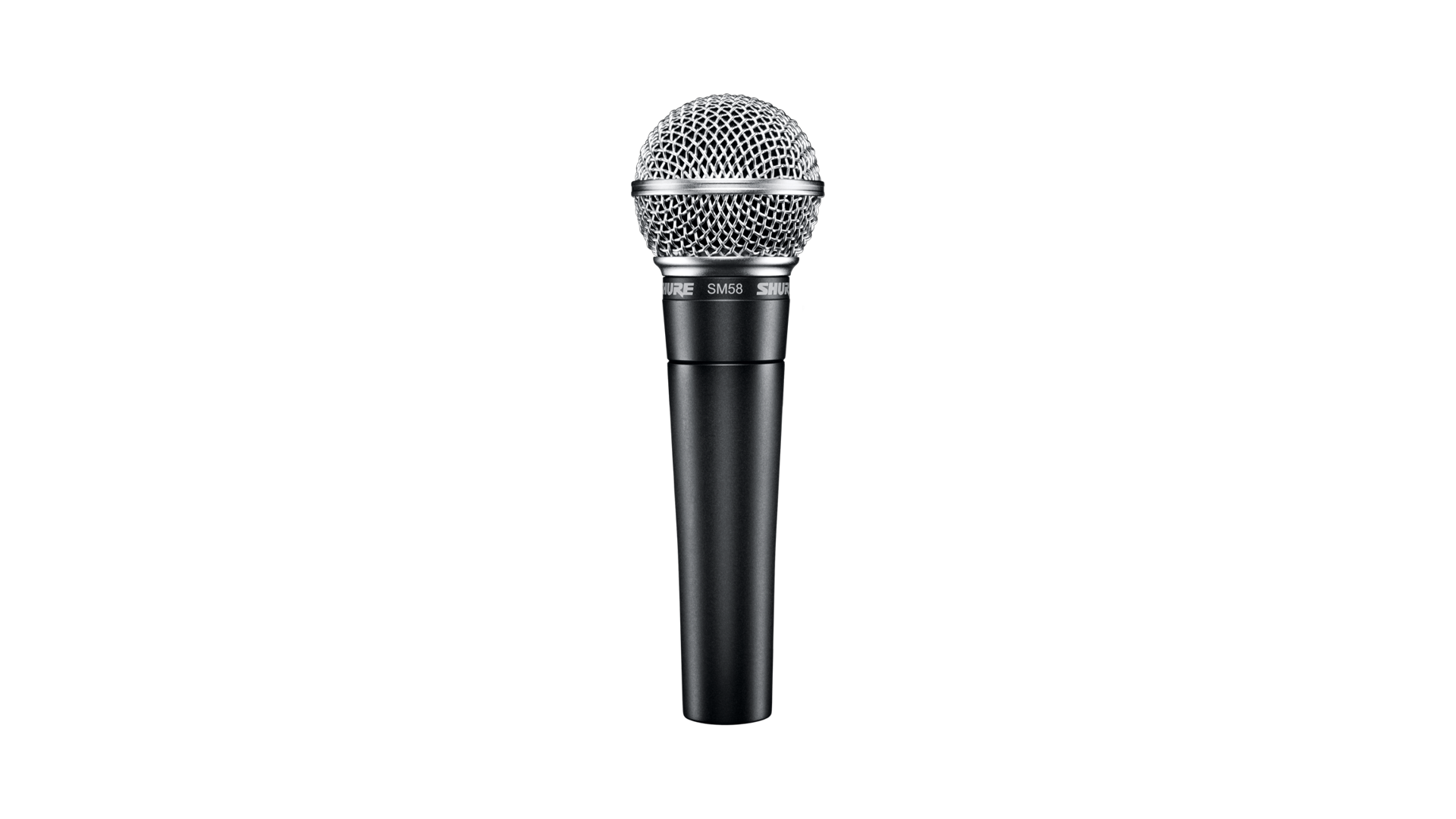

A microphone is an input device that converts sound waves into electrical audio signals, digitized by a sound card or built-in converter. Types include dynamic (robust, for vocals/instruments), condenser (sensitive, for studio recording), USB (plug-and-play), wireless (Bluetooth/RF), headset (integrated), and Lavalier (clip-on). Features noise cancellation, directional patterns (cardioid, omnidirectional). Essential for voice input, recording, conferencing, and accessibility.
- Application: Voice recording, voice commands, video conferencing, podcasting, gaming, dictation, accessibility tools.
Electronic Cards Based Devices
Exam Question Alert: Electronic card-based devices can be a short note question. Understand their function and examples.
Electronic card-based devices are input peripherals designed to read and sometimes write data stored on various types of cards. These devices are integral to modern security, identification, and transaction systems, providing a convenient and often secure method for data input. They are widely used in banking, access control, public transport, and telecommunications.

- Smart Card Readers: These devices are used to read data from smart cards, which are typically credit-card sized plastic cards embedded with an integrated circuit (microchip). This microchip can store and process data, making smart cards highly secure for applications like payment systems (e.g., EMV bank cards), mobile phone SIM cards, national ID cards, and access control systems. The reader establishes a connection with the chip to exchange information.

- Magnetic Stripe Readers: Magnetic stripe readers are designed to read data encoded on a magnetic stripe, usually found on the back of plastic cards. This technology is older than smart cards but is still widely used for credit cards, debit cards, loyalty cards, and hotel key cards. The reader works by swiping the card through a slot, allowing a read head to interpret the magnetic data.

- RFID Readers (Radio-Frequency Identification Readers): While not explicitly mentioned in the original list, RFID readers are increasingly common electronic card-based devices. They read data from RFID tags (which can be embedded in cards) using radio waves, without requiring physical contact. Applications include contactless payment systems, inventory tracking, and access control.
Speech Recognition Devices
Exam Question Alert: Be prepared to explain the application areas of speech recognition devices.
Speech recognition devices and software systems enable computers to identify, interpret, and respond to the sound of spoken words. This technology converts spoken language into text or commands, allowing users to interact with computers using their voice. It has become increasingly sophisticated, moving beyond simple command recognition to understanding natural language.
- Application:

- Voice Control Systems: Personal assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon Alexa allow users to control devices, search for information, set reminders, and perform various tasks using voice commands.

- Dictation Software: Programs such as Dragon NaturallySpeaking enable users to convert spoken words directly into written text, significantly speeding up document creation for professionals, writers, and individuals with typing difficulties.
- Accessibility Tools: Speech recognition provides crucial accessibility for individuals with disabilities, allowing them to operate computers and communicate more effectively.
- Telephony and Customer Service: Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems use speech recognition to guide callers through menus and provide automated assistance, improving customer service efficiency.
- Medical Transcription: Doctors can dictate notes directly into patient records, streamlining administrative tasks and improving accuracy.
- Automotive Systems: Voice commands are used in cars for navigation, controlling entertainment systems, and making calls, enhancing safety by reducing driver distraction.
Vision Based Devices (Digital Camera and Video Input)
Vision-based devices capture visual data and convert it to digital format for computer processing. Include sensors like CCD/CMOS for light-to-electric conversion.
- Digital Camera/Webcam: Digital cameras capture still images/video with lenses, sensors (CCD/CMOS), resolution in megapixels (MP). Webcams are integrated/external for video calls, streaming. Features autofocus, zoom, image stabilization. Connected via USB, WiFi. Used in photography, surveillance, conferencing.
- Image Scanners: Convert physical documents/photos to digital images. Types: flatbed (stationary), sheet-fed (automatic), handheld (portable). Resolution in DPI (dots per inch), color depth (bit). Features OCR integration, duplex scanning. Used for archiving, digitization.
4.2 The Output Accessories
Output accessories are peripheral devices used to display or present processed data (information) from the computer to the user in a human-readable or usable format.
Monitor (Visual Display Unit - VDU)
Exam Question Alert: Expect questions differentiating between types of monitors (e.g., CRT vs. LCD) and discussing softcopy output devices.
The monitor, also known as a Visual Display Unit (VDU), is the primary output device for displaying visual information (text, graphics, and video) generated by the computer. It provides a "softcopy" output, meaning the display is temporary and not physically printed. Monitors are essential for user interaction, allowing us to see the results of our commands and the output of applications in real-time.
- Types:

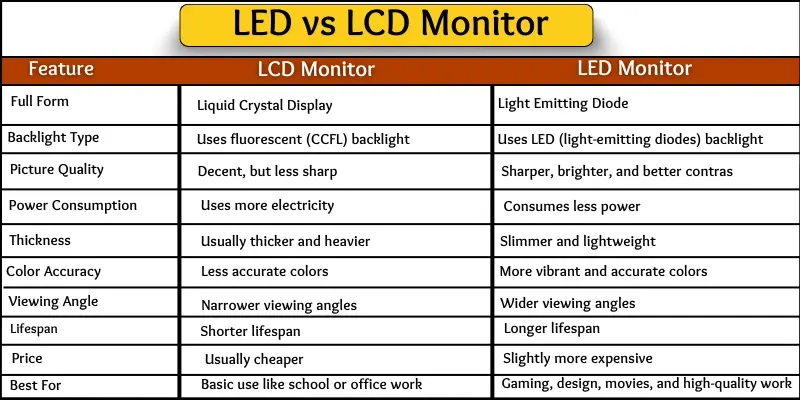
- CRT (Cathode Ray Tube): An older technology that uses an electron beam to illuminate phosphors on a screen. CRTs are bulky, consume more power, and have largely been replaced by newer technologies.

- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): Uses liquid crystals to block or pass light from a backlight, creating images. LCDs are thinner, lighter, and more energy-efficient than CRTs.

- LED (Light Emitting Diode): Essentially a type of LCD monitor that uses LEDs for backlighting, offering improved contrast, color accuracy, and even greater energy efficiency.

- OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode): Each pixel in an OLED display emits its own light, allowing for perfect blacks, infinite contrast, and very thin designs. They offer superior image quality but can be more expensive.
- Key Characteristics:
- Resolution: The number of pixels (picture elements) displayed on the screen, determining the sharpness and detail of the image (e.g., 1920x1080 for Full HD). Higher resolution means more detail.
- Refresh Rate: The number of times per second the display updates its image, measured in Hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate (e.g., 120Hz, 144Hz) results in smoother motion, especially important for gaming and fast-paced video.
- Size: Measured diagonally across the screen, typically in inches.
- Aspect Ratio: The proportional relationship between the width and height of the screen (e.g., 16:9 for widescreen, 4:3 for older displays).
- Response Time: The time it takes for a pixel to change from one color to another, measured in milliseconds (ms). Lower response times reduce motion blur.
Printer
Exam Question Alert: Differentiating between impact and non-impact printers is a common question.
A printer is an output device that produces a physical, "hard copy" of documents and images generated by the computer. It converts digital data into printed text and graphics on paper or other physical media. Printers are essential for creating tangible records, sharing information in physical format, and producing professional documents.
- Impact Printers: These printers create an image by physically striking an inked ribbon against the paper. They are generally noisier but can produce carbon copies.
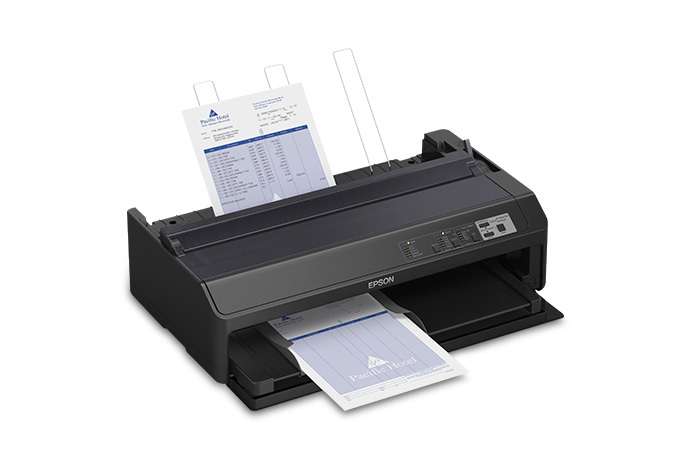

- Dot Matrix Printers: Use a print head that moves back and forth, or in an up and down motion, and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper. They are known for their durability and ability to print multi-part forms.
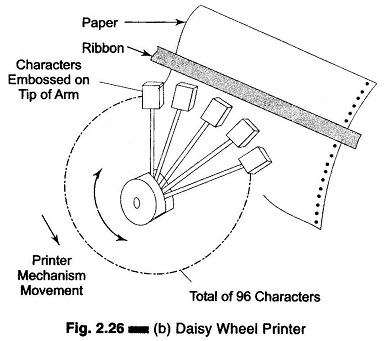
- Daisy Wheel Printers: Use a "daisy wheel" element that contains pre-formed characters. A hammer strikes the character against the ribbon and paper. They produce high-quality text but cannot print graphics.
- Non-Impact Printers: These printers create characters and graphics on paper without any physical contact between the printing mechanism and the paper. They are generally quieter and produce higher quality output.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/printer-649004582-31623906dc38475bba79c63b0d18d761.jpg)
- Inkjet Printers: Create images by propelling droplets of ink onto paper. They are popular for home and small office use due to their ability to print both text and high-quality color graphics.

- Laser Printers: Use a laser beam to create an image on a photosensitive drum, which then attracts toner (powdered ink). The toner is transferred to the paper and fused with heat. Laser printers are known for their high speed, high-quality text, and cost-effectiveness for high-volume printing.

- Thermal Printers: Use heat to produce an image on heat-sensitive paper. Commonly used for receipts and labels.

Plotter

A plotter is a specialized output device that produces vector graphics on paper or other media using pens. Unlike printers, it draws lines continuously rather than rasterizing pixels. Types include pen plotters (drum or flatbed), cutting plotters (for vinyl signs), and electrostatic plotters. High precision for technical drawings. Connected via serial, USB, or network. Used in engineering, architecture, GIS.
- Application: CAD (Computer-Aided Design), map making, large-scale posters, blueprints, banners.
GPS (Global Positioning System)
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system providing location, velocity, and time data. A GPS receiver acts as an output accessory, interfacing with computers via USB or Bluetooth to feed data into mapping software, navigation apps, or GIS systems. Provides real-time coordinates (latitude/longitude), altitude, speed. Used in vehicles, hiking, fleet management, and geolocation services.
Projectors

A projector is an output device that displays computer video output on a large screen or surface. Types include LCD (liquid crystal), DLP (digital light processing), LED/Laser (energy-efficient). Key specs: resolution (HD, Full HD, 4K), brightness (lumens), contrast ratio, throw distance. Connectivity: HDMI, VGA, USB. Portable or fixed installation. Used for presentations, home theaters, classrooms.
- Application: Presentations, movie viewing, large-group instruction, gaming, advertising.
Headphones & Speakers

Audio output devices that convert digital signals to sound waves. Headphones: worn over/on/in ears for private listening. Types: over-ear (comfortable, noise isolation), on-ear (compact), in-ear (portable), wireless (Bluetooth), with active noise cancellation (ANC). Speakers: external for shared listening, 2.1/5.1 surround sound, powered or passive. Connected via 3.5mm jack, USB, Bluetooth. Used for music, gaming, calls, multimedia.
Soundcard/Video Card
Internal expansion cards or onboard components for audio and video processing.

- Sound Card: Processes audio signals from digital to analog, supports multiple channels (stereo, surround), sample rates (44.1kHz-192kHz), interfaces (3.5mm, optical). Onboard or discrete (e.g., Creative Sound Blaster) for high-quality audio, gaming, music production.
- Video Card (GPU): Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) renders images/video. Specs: VRAM (GDDR), clock speed, CUDA cores. Interfaces: HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA. Dedicated GPUs (NVIDIA, AMD) for gaming, CAD, video editing; integrated in CPUs for basic tasks.
Voice Response System (Text-to-Speech)
Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems convert written text into spoken audio using synthesis algorithms (concatenative, formant, articulatory). Engines like eSpeak, Google TTS, Amazon Polly provide natural voices, adjustable speed/pitch. Used in screen readers for visually impaired, IVR systems, audiobooks, voice assistants.
- Application: Interactive voice response (IVR) systems, accessibility tools, navigation, education.
Computer Output Microfilm (COM)

COM is a specialized output technology that records computer data directly onto microfilm or microfiche using laser beams. Produces high-density, durable archival copies. Film stores thousands of pages compactly, resistant to environmental damage. Used for long-term data preservation in libraries, government, legal archives.
SGD (Speech Generation Device)
Speech Generation Devices (SGDs) are augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools for individuals with speech impairments. Include text-to-speech synthesizers, symbol-based systems (e.g., picture boards), and eye-tracking interfaces. Portable or fixed, with customizable voices. Used by people with ALS, cerebral palsy, etc., to communicate verbally.
4.3 Ergonomically Designed Devices
Exam Question Alert: Expect questions on the importance and examples of ergonomically designed devices and how they enhance user efficiency.
Ergonomics is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions among humans and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data, and methods to design in order to optimize human well-being and overall system performance. In the context of computing, ergonomically designed devices and workstations aim to reduce user fatigue, discomfort, and the risk of long-term health issues (such as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, repetitive strain injuries, and back pain) by optimizing the interaction between the user and their computer equipment. This leads to increased efficiency, productivity, and a healthier work environment.
- Ergonomic Keyboards: These keyboards are designed to promote a more natural hand and wrist position. Examples include split-design keyboards that separate the keys into two or more sections, negative tilt keyboards that angle downwards away from the user, and those with integrated padded wrist rests. These features help reduce strain on wrists and forearms, minimizing the risk of conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Ergonomic Mice: Designed to fit the natural contours of the hand and keep the wrist in a neutral "handshake" position. This category includes vertical mice, trackball mice (where the ball is manipulated by the thumb or fingers), and contoured mice with specialized grips. They aim to reduce wrist pronation and repetitive movements.
- Adjustable Monitors: Ergonomic monitors offer a wide range of adjustments, including height, tilt, swivel, and pivot. This allows users to position the screen at an optimal eye level, preventing neck and eye strain, reducing glare, and promoting a comfortable viewing angle.
- Ergonomic Chairs and Desks: These are fundamental to an ergonomic workstation. Ergonomic chairs provide adjustable lumbar support, seat height, armrests, and backrest recline to support the natural curve of the spine and promote good posture. Adjustable desks (sit-stand desks) allow users to alternate between sitting and standing positions, reducing the negative effects of prolonged sitting.
- Document Holders: Position documents at the same height and distance as the monitor to reduce neck and eye movement.
- Footrests: Support feet and promote proper leg circulation, especially for users whose feet don't comfortably reach the floor.
Key Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users: Adhering to these guidelines can significantly improve comfort and reduce health risks associated with prolonged computer use:
- Posture: Maintain a neutral posture with a straight back, shoulders relaxed, feet flat on the floor (or on a footrest), and arms parallel to the floor. Elbows should be at a 90-degree angle.
- Monitor Distance and Height: Position the monitor at arm's length (about 20-40 inches) from your eyes, with the top of the screen at or slightly below eye level. This prevents neck strain and reduces eye fatigue.
- Breaks: Take frequent short breaks (e.g., every 20-30 minutes) to stand up, stretch, and rest your eyes. The 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) can help reduce eye strain.
- Lighting: Ensure adequate and glare-free lighting to prevent eye strain. Avoid direct glare on the screen from windows or overhead lights.
- Input Device Placement: Keep the keyboard and mouse close to your body to avoid overreaching, which can strain shoulders and arms.
Course Code: CMP 116
Credit Hours: 3
This unit provides comprehensive knowledge about computer input/output accessories and the importance of ergonomic design.
Important Questions
- What is an Input Device? Explain different types of Data Scanning Devices. (8)
- Differentiate between softcopy and hard copy output devices. Explain different types of monitors used in today's market. (7)
- Troubleshoot vision based and speech recognition devices along with diagram. (7)
- What is softcopy output device? Differentiate between CRT and LCD Monitor. (7)
- What do you mean by peripheral devices? Explain any five output devices. (10)
- How do ergonomically designed devices increase efficiency of computer users? Explain in brief. (5)
- What is a printer. Differentiate between ink jet and dot matrix printer. (7)
- Write short notes on: (Any two)
- Electronic card-based devices
- Vision based devices
- Speech recognition devices
